Departement van Waterwese en Bosbou
Ons lewe in ‘n tydperk van globalisasie en waar kwaliteit tyd nie meer bestaan nie. Waar is die dae toe ons nog die prag van die natuur om ons waargeneem het?
As jy vassit in die verkeer, sien jy nog die wonderwerke van ons Skepper om ons raak? My antwoord is onwillekeurig nee. Ons lê op ons toeters vir die stadige trok voor ons om na die linkerbaan toe te beweeg, sodat ons kan verbysteek en jaag na ons volgende afspraak. Ons kla so graag as die wonderlike reëndruppels begin val want net gister is my motor gewas. En dan aan die anderkant, watter ongelooflike gevoel om kaalvoet in die reën te dans. Die bekoring van nuwe lewe, geure en kleure na die eerste reënval is diep in my geheue vasgeprent. As jong dogtertjie sal ek nooit die ritme van reëndruppels op die grondpad vergeet nie, daarvan dan my bynaam ”Kaalvoetklonkie”
Soos die koms van elke nuwe seisoen, met nuwe groei en verwagtinge besef ek weereens watter groot rol die Departement van Waterwese en Bosbou beter bekend as DWAF speel.
DWAF is die bewaarder van Suid-Afrika se water en bosbouhulpbronne. Dit is hoofsaaklik verantwoordelik vir die formulering en implementering van beleid wat hierdie twee sektore beheer. Dit het ook die verantwoordelikheid vir waterdienste wat deur die plaaslike regering verskaf word. Terwyl hulle strewe om te verseker dat alle Suid-Afrikaners toegang tot skoon water en veilige sanitasie verkry, ontwikkel die watersektor ook effektiewe en doeltreffende waterhulpbronbestuur om ekonomiese en sosiale ontwikkeling te verseker. Die bosbouprogram handhaaf ook die bestuur van die land se natuurlike bosbronne en kommersiële bosbou vir die blywende voordeel van die land.
DWAF het talle projekte / programme en Tenders gelys wat waardevol vir ons kliënte kan wees.
Hier is slegs ‘n paar Projekte wat op hul webwerf genoem is, naamlik:
+ Groot Letaba Water Development Project
+ Groundwater
+ Hydrology (Data, Dams, Floods and Flows)
+ Integrated Water Planning Portal – Strategy Portal
+ Integrated Water Resource Planning
+ Integrated Water Quality Management Plan (IWQMP) For The Olifants River System
+ Integrated Water Quality Management Strategy
+ Lusikisiki Regional Water Supply Scheme
+ Mokolo and Crocodile River (West): Water Augmentation Project (MCWAP)
+ Mzimvubu Water Project
Ons weet beide water en bosbou speel ‘n groot rol in ons lewens. Indien nie die grootste nie. Ons neem dikwels ons pragtige land as vanselfsprekend en daarom moet ons ook die verantwoordelikheid neem om water te bespaar en na ons bosbou te kyk.
Ek kan boeke en verhale skryf oor die onderwerp, maar gaan net so vlugtig ‘n paar goedjies noem. Ek sal ‘n bietjie van alles skryf, so jy sal beslis iets interessants vind om te lees.
Lekker “het jy geweet” feite?
- Het jy geweet as jy 5 minute stort, in plaas van bad, sal slegs sowat ‘n derde van die water gebruik word. Dit kan in ‘n week tot 400 liter water bespaar.
- As jy verkies om te bad eerder as om te stort, moenie die bad op die rand vul nie. ‘n Bad gebruik tussen 80 en 150 liter water per bad.
- Het jy geweet Internasionale Bosdag val presies dieselfde dag as Menseregtedag in Suid-Afrika, dus word dit meestal geïgnoreer.
Fassinerende Gesondheid feite oor water:
- Slegs 1,1% van die water op aarde is geskik om te drink soos dit is.
- Ons liggame bestaan uit 55 – 75% water.
- Depressie en moegheid kan dikwels die simptome van dehidrasie wees.
- Dit is gesond om water met etes te drink, aangesien dit die verteringsproses bevorder
- Die beste manier om ontslae te raak van waterretensie is om baie water te drink. Water retensie kan ‘n teken van dehidrasie wees.
- Water laat die liggaam toe om vette meer doeltreffend te metaboliseer.
- Goeie water inname verhoed dat die vel sak.
- Water is die hoofvoedsel wat die liggaam benodig.
- Die dorsrefleks kom slegs voor wanneer ons liggame reeds gedehidrier is.
- Kinders dehidreer vinniger as volwassenes, ‘n opname het getoon dat 65% van die skoolkinders te min water drink.
- ‘n 2% vermindering van die water vlakke in die liggaam kan lei tot ‘n 20% afname in geestelike en fisiese prestasie.
- Dehidrasie kan kontraksies in swanger vroue veroorsaak.
Vyf feite rakende die bosboubedryf
- Natuurlike woude dek ‘n derde van alle grond op aarde. Soos ons weet, absorbeer bome koolstofdioksied en gee suurstof vry, wat die absolute noodsaaklikheid van ons voortbestaan maak.
- Plaaslik is slegs 0,4% van ons landmassa gedek deur natuurlike woud. Dit is net 500 000 ha, ondersteun deur 39 miljoen hektaar wat deur savanne stelsels gedek word.
- Daar is drie hooftipes bome wat op Suid-Afrikaanse plantasies groei. Hulle is dennehout (44%), Eucalyptus (44%) en Wattle (12%).
- Die Suid-Afrikaanse bosboubedryf het 158 000 mense in diens en is verantwoordelik vir 11% van die land se landbou-BBP en 5% van die BBP.
- Daar is sowat 26 000 houtkwekers in Suid-Afrika. Dit sluit in die groot multinasionale korporasies, die regering en duisende kleinskaalse maatskappye.
Laaste maar nie die minste nie….
Dit is goed om ons self ‘n bietjie meer wys te maak op ons reënvalle en damwatervlakke. Ons sien dikwels dat iemand iets oor hul watervlakke op Facebook plaas.
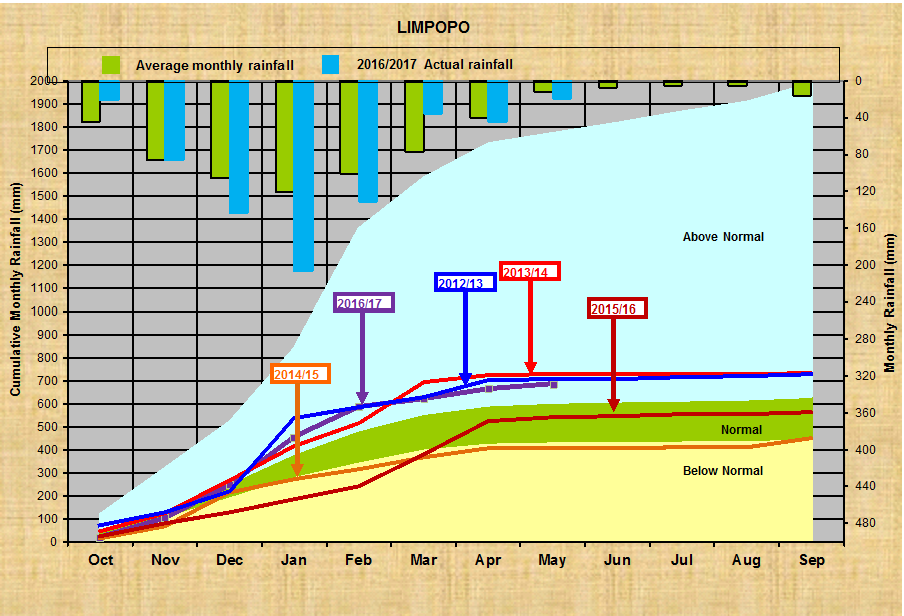
Wel, ek gaan jou ‘n paar interessante grafieke van ons Provinsiale Reënval asook ons Dam vlakke wys. Spesiaal vir die ernstige hengelaars daar buite. Ken jou watervlakke!
Gauteng:
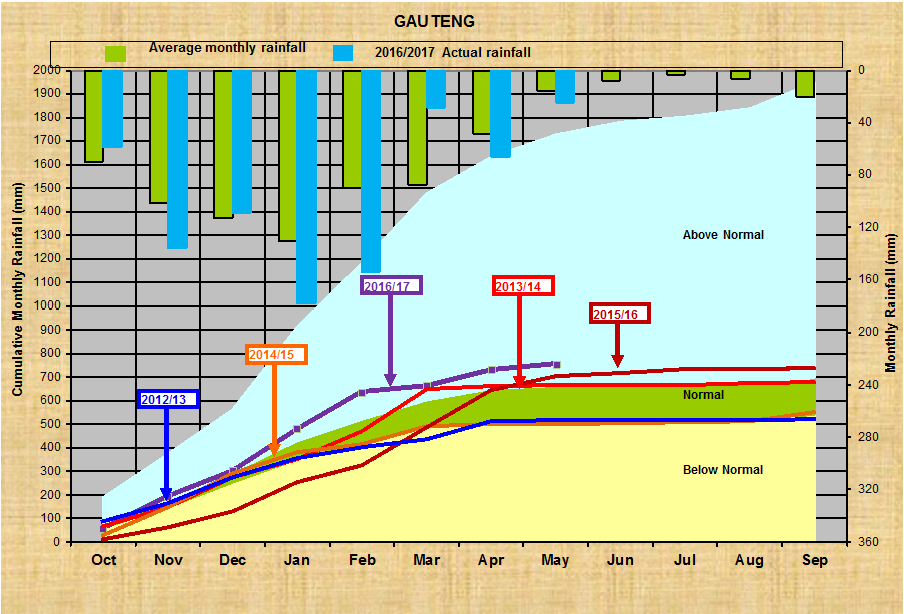
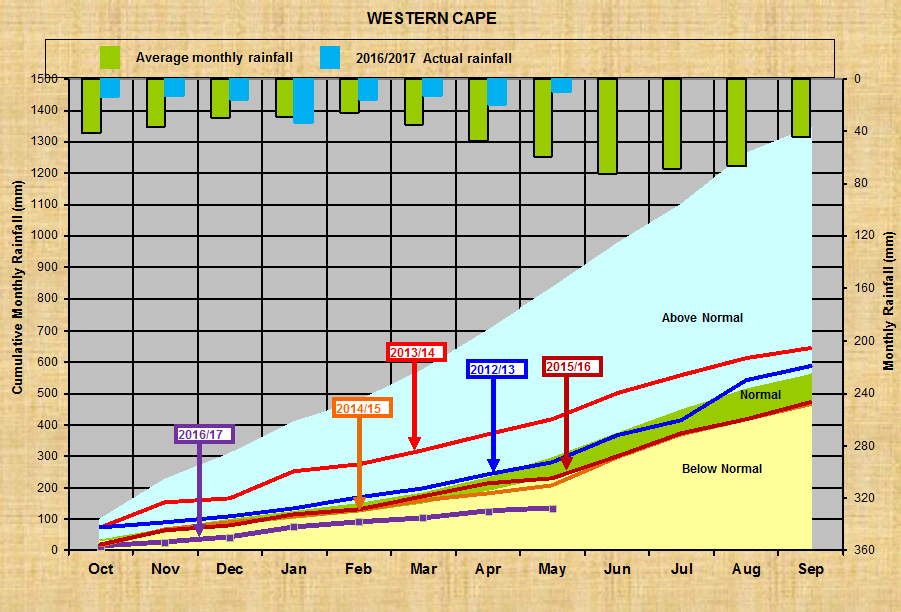
Wes-Kaap:
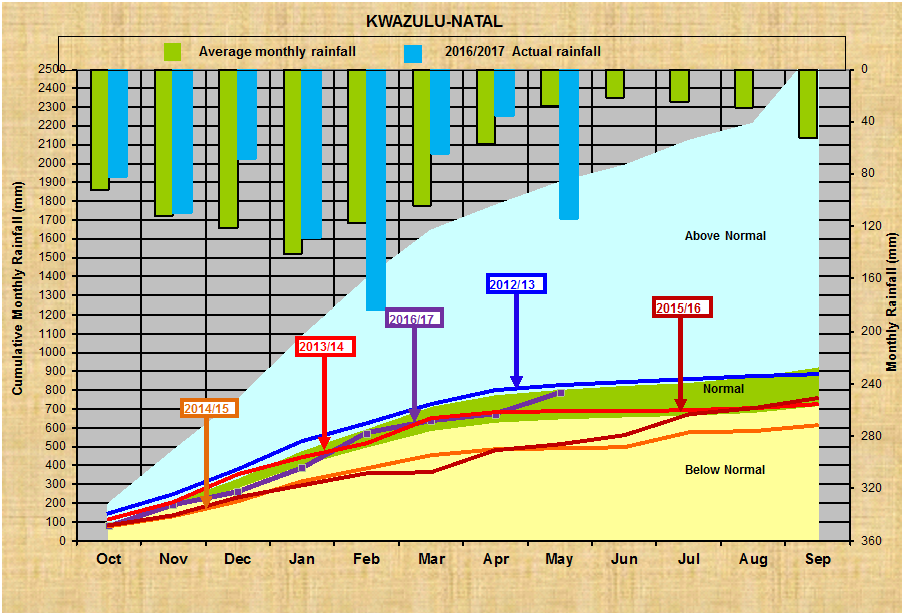
KwaZulu-Natal:
Noord-Kaap:
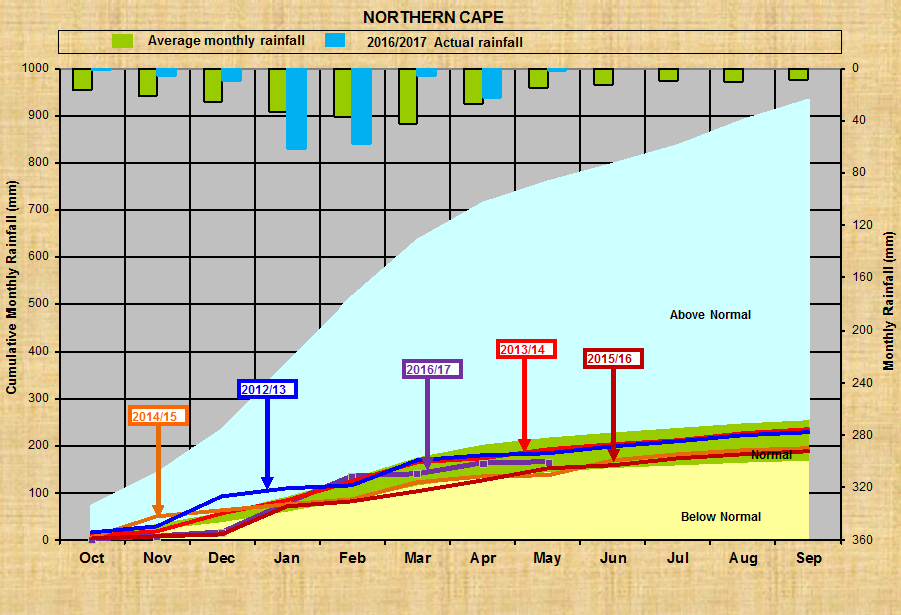
Oos-Kaap:
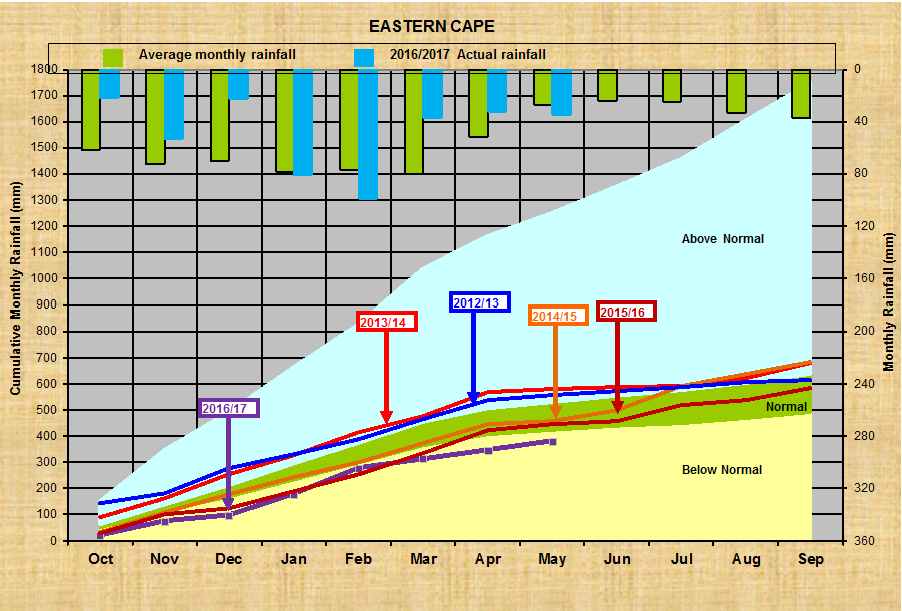
Vrystaat:
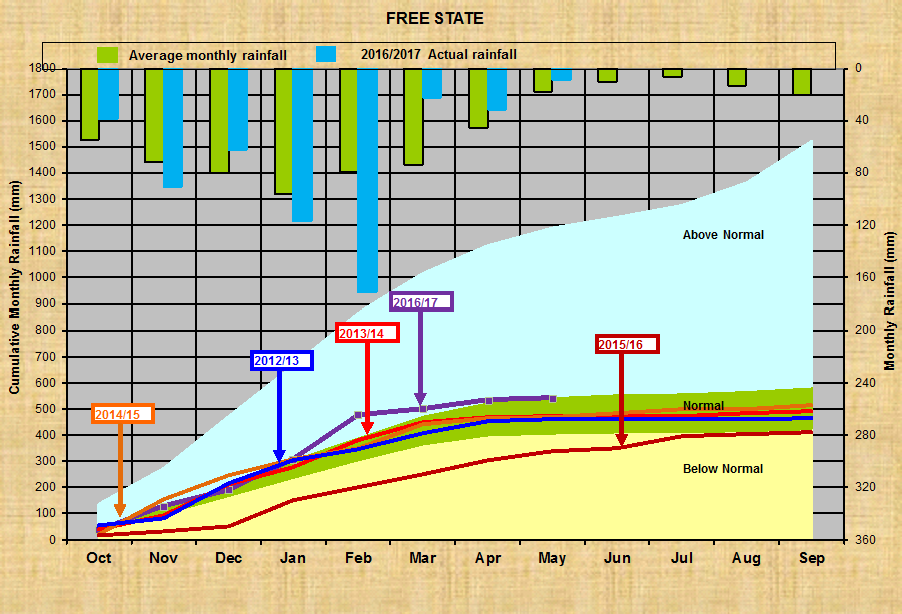
Noord Wes:
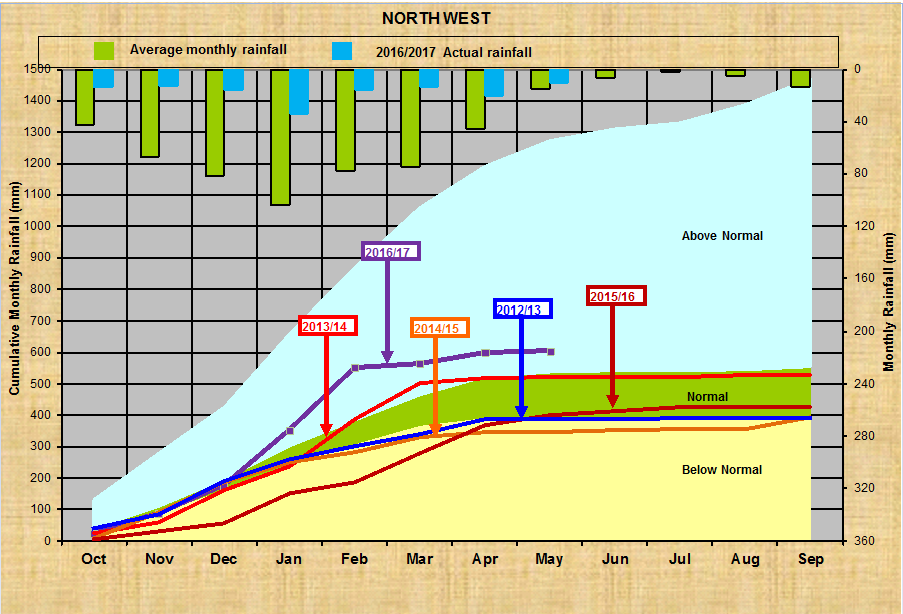
Mpumalanga:
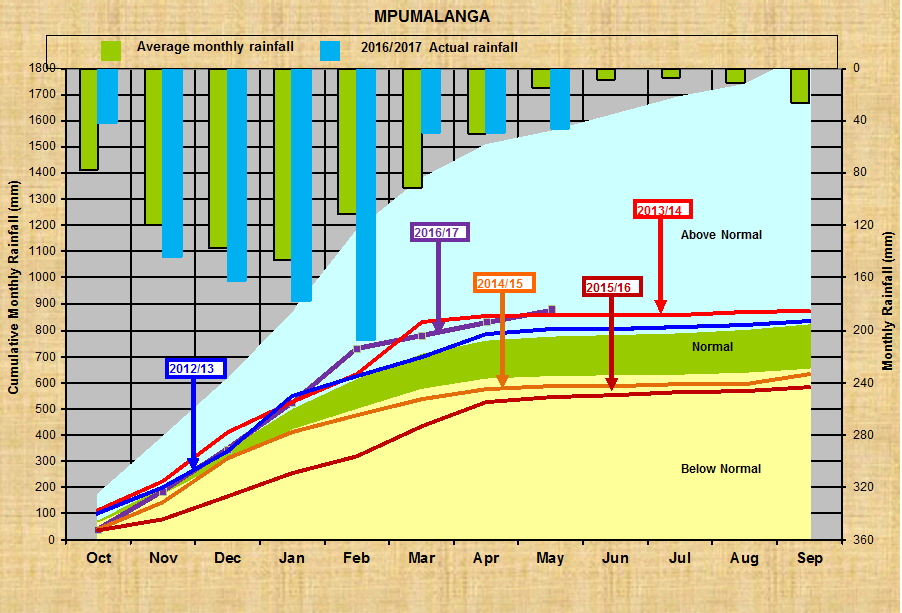
Limpopo:
Provinsiale Dam en Rivier watervlakke
Data laas opgedateer
2017-08-07
Volle kapasiteit in miljoen kubieke meter
Wes – Kaap
=1867.0
Noord – Kaap
=145.5
Oos – Kaap
= 1832.4
Vrystaat
= 15968.0
Noord Wes
= 15968.0
Mpumalanga
= 2538.8
Limpopo
= 1522.3
Kwazulu- Natal
=4782.7
Gauteng
=114.8
Onthou, elke druppel water tel, en dink voor jy op ‘n stukkie papier ink!
Bronne
DWAF
http://www.preventionweb.net/organizations/937
Projekte / Programme
http://www.dwaf.gov.za/projects.aspx
Tenders
http://www.dwaf.gov.za/Tenders/tendersCurrent.aspx
Water Feite
http://www.health24.com/Diet-and-nutrition/Beverages/12-interesting-water-facts-20120721
Forestry
http://www.countrylife.co.za/wild-earth/32929
http://www.fao.org/docrep/005/ac486e/ac486e02.htm#TopOfPage
Rainfall pictures
http://www.dwaf.gov.za/hydrology/Provincial%20Rain/Default.aspx
Dam levels
http://www.dwaf.gov.za/hydrology/Weekly/Province.aspx
If you are interested in becoming one of our subscribers, please visit our website.
To view notes with screenshots on how to use our website, please visit our Wiki site.
To view more articles, please visit our blog.
About Christine Brooks
My journey started in 2015 with Leads 2 Business, as an Account Executive, and gradually grown to take the role of being the Client Liaison Officer (CLO) since 2018. Assisting in the delivery of our services and insuring our clients expectations and requirements are exceeded.