“Oh, Sh#$, My Mask!” – Normal Person on the Daily.

I know we don’t all particularly like change, but times have changed and we, therefore, need to embrace change as well and conform to the new norm and try to remember to wear a mask and sanitize all the time.
The health and safety within the construction industry is challenging at the moment as everyone has to try to adapt to the new way of working.
To reduce the impact of the COVID-19 outbreak, plans need to be in place to help identify risk levels in the workplace. They also need to determine the implementation of control measures.
Owners of companies as well as their staff need to remain in the know and up to date with the changing Covid-19 outbreak conditions as they directly affect and relate to community spread of the virus.
This blog is on “Changes since COVID-19” within the Construction industry. I’d like to focus on the construction site itself.
As a Health & Safety officer onsite or the main contractor, you will need to assess the hazards to which your workers may be exposed. You also need to then evaluate the risk of exposure and ensure workers adhere to rules in place to prevent exposure.
Conducting a job hazard analysis can also help you determine whether work activities require close contact (within 2 meters) between staff, visitors, customers or members of the public.
There is so much information on this particular topic, however, below are some points which I believe most stood out to me:
1. Personal Protective Equipment
- To be honest, most construction workers are unlikely to need more PPE beyond what they already use. What I mean is that the PPE that they should already have to have is a hard hat, gloves, safety glasses, and a face mask. Since Covid-19, the PPE required may now include eye protection, gloves, and/or face shields.
2. Transportation
- Washing your hands before and after using public transport. Also washing your hands and sanitizing as soon as you get home. All persons should ensure that their hands are sanitized before and after, entering and existing any vehicle.
- The use of individual transport is much preferred during this crisis. Where possible, workers should use their cars and drive alone rather than collective or make use of public transport. The employer can facilitate this and assist by ensuring there is a car park or open site available to all employees. If you think about it, even a rack for securely storing bicycles would also help. Heck if you live close enough and are fit do to so, then walk to work.
- The contractor or health & safety consultant should note and assess the number of workers being transported. A log should be kept and the consultant can also implement measures to ensure that social distancing between persons is adhered to.
- Work buses or work transport should have space where people can sit apart from each other (adhering to social distancing) and the vehicle should be well-ventilated. Masks are to be worn in both public transport & employer transport/buses.
- Visitors to the construction site should be discouraged to visit. Should there be a delivery of any sort, drivers should try to remain in their vehicles while being screened and provided with hand sanitizer. When goods are being delivered, it is suggested to do so through pick-up or delivery outside of the construction site. It’s not often, but delivery workers could also be allowed to use facilities such as toilets and cafeterias onsite, and these should be sanitized and cleaned thoroughly at all times.
- Transportation of staff:
- Vehicles being used to transport workers or being used on site are to be thoroughly disinfected each time before and after boarding
- Each person onsite is to be screened and have their temperature taken twice daily. A log of the everyone’s details, temperatures, times and dates as well as those of visitors to the site will need to be kept.
- Stickers or markings on the ground should be placed around the site to ensure social distancing.
- Wearing of masks is mandatory
- The appointed Covid19 officer on site would need to monitor staff as they disembark from any transport vehicle to make sure social distancing and sanitizing are done.
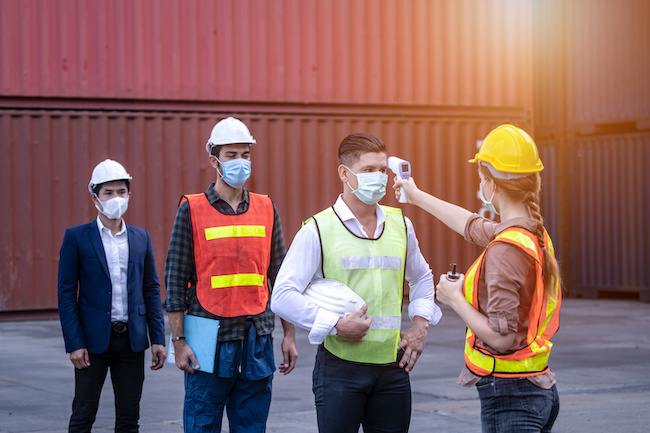

3. Site access & workspace
Contractors have specific responsibilities for health and safety and must coordinate all activities of workers & sub-contractors. They are responsible for ensuring the health and safety of everyone and would do so by implementing policies and procedures as well as providing workers with instructions, training and supervision.
It is recommended that a Covid-19 safety co-ordinator or officer be appointed at each site and that everyone is familiar with that person. This officer will ensure compliance with Covid19 regulations and safeguard against infection as well as be able to provide answers to any questions persons may have.
- Covid-19 compliance procedures are to be included in the contractors existing safety manuals onsite.
- Site safety manuals should highlight where Covid19 safety procedures are difficult to adhere to, depending on the nature of work. (eg: shared fall protection ropes, tools and equipment that could be potential transmission points)
- Covid19 signage and posters in all languages necessary should be installed onsite. Especially in high traffic areas such as entries, exits, hallways, meeting points, material docks, canteens and changing rooms.
- Adopt staggered work schedules – alternating workdays or extra shifts, to reduce the total number of employees on a job site at any given time and to ensure physical distancing.
- Ensure clean toilet and handwashing facilities. Clean and disinfect portable site toilets regularly. Fill hand sanitizer dispensers regularly. Disinfect frequently touched items such as door handles, soap dispensers, taps and toilet seats.
4. Lunchrooms / Eating Area
- Stagger lunch hours to reduce the number of staff in the breakroom at one time.
- Food should be consumed at designated areas only. When you are eating, your mask is off and the risk of infection may be greater. Social and safe distancing still applies.
- As said before, signage should be in the lunch area creating Covid19 awareness or simply just reminding everyone to wash your hands and wear your mask. Remember this is sort of “new” to us, and its human nature to forget to wear your mask sometimes. 6 months of it and I’m still not 100% used to it, but we have to be. I appreciate the signs and reminders.
- Seating arrangements now needs be modified to include social distancing.
- Tables, chairs, microwaves, utensils and any other equipment or surfaces need to be disinfected before and after every use. Where possible, encourage staff to bring their cutlery and crockery and to keep this at their desk or in their locker.

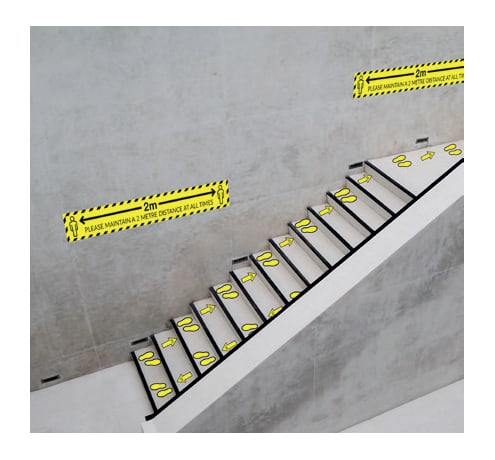
5. Staircases
- One-way walking on the staircase should be implemented. Basically, have people keep left at all times. This is to avoid social distancing being compromised.
- The handrail needs to be regularly disinfected and should you use this you need to sanitise before and after use. Staff shouldn’t touch anything.

6. Site Offices
- Again, Covid19 signage needs to be up at the site office as well as “Restricted Access” so that they know there is a limit to the number of people allowed in that area.
- Sinks need to be installed with hand sanitizer available for staff and visitors
- A checklist of commonly used items should be drawn up and those need to be wiped and clean periodically (such as doorknobs, chairs, desks, stationery). The construction safety officer is to ensure this is complied with.

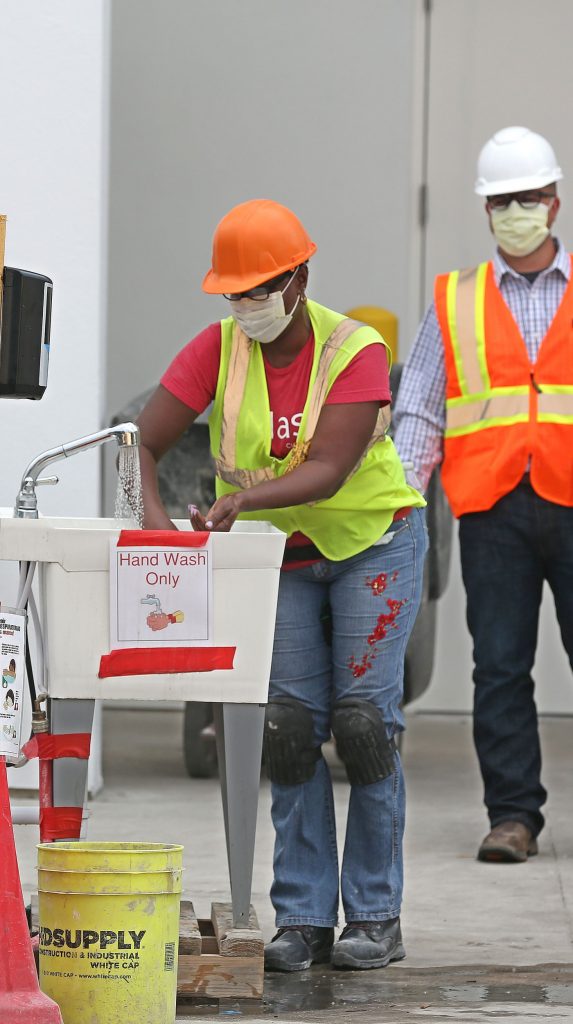
7. Site Sanitation Measures
- Provide hand sanitizers/handwash and sinks with clean running water.
- Provide paper towels instead of hand towels. This you can throw away after use, instead of all using the same, dirty hand towel.
- Provide foot-operated/foot pedal rubbish bins in all bathrooms and site offices.
- Limit the number of persons allowed to make use of the toilet facilities at any one time. Have a visible sign with the maximum capacity allowed.
- Toilet facilities and fixtures are to be disinfected by cleaning staff regularly.

8. Material Management
1. Unloading and loading zones should be clearly marked and also have limited access.
2. Any vehicle entering or exiting the premises is to be disinfected. Especially machinery or vehicles used by multiple persons.
3. Documents are to be reviewed and validated in digital formats where possible. If you can fill in contracts or documents online then do so. This is to avoid the physical exchange of paperwork and avoid the spread of the virus.
4. Any delivery that is unloaded should be disinfected before storage at the site.
9. Training & Awareness is to be provided to all employees on the following:

- Signs and symptoms of COVID-19 and the need to report any safety and health concerns
- All policies and procedures are to be followed
- Hygiene and social distancing
- Avoiding physical contact with others and maintaining a distance
- Appropriate cleaning practice
- The proper way to cover coughs and sneezes
- Alternatives to shaking hands upon entry
- Not touching your face, or anyone else’s
- Decontamination, removal and disposal of any PPE being used
- The importance and seriousness of staying at home if you are sick.
- Wearing a mask, always
- Any members who have been in isolation, quarantine or had been diagnosed with COVID-19 should be physically separated from any other members of the team. Be it in a different room or on a different part of the site. You can even use closed doors or walls as physical barriers to separate workers.
10. Reporting
- A team which includes a safety officer could be put together to form a Covid19 response unit onsite. This team can then plan, co-ordinate and provide information to others. They would be involved in decision making and co-ordination with other companies and stakeholders.
- Daily, weekly, fortnightly and monthly reports should now include Covid19 stats. This means Covid19 safety compliance as well as staff screening. The number of workers being screened, their locations and any workers suspected of symptoms.
- Site safety procedures are to be updated and managed.
- Documents, including training logs, should be kept and readily available.
- A three strike policy could be implemented for those who are non-compliant. In the same breath, you can implement a rewards program for those who have done well and adhered to the rules.
- Meetings. Keep in-person meetings as short as possible and limit the number of workers in attendance. Limit this to less than 15 minutes and use social distancing practices. No more than 50 persons gathered in the same area. If you have to, rather consider holding on-site meetings in open spaces or outside. Another alternative is having staff or team meetings online.
11. Engineering Controls
- Plastic sheets can be used as barriers
- Special attention needs to be given to those “High Risk” employees as well as those with family members who are at high risk.
12. Use of Technology
- Thermal imaging scanners can be used for easy temperature screening of groups of staff.
- Digital scanners (instead of biometrics) can be used for recording staff attendance.
- Drones. I’ve even heard people go as far as to use drones to spray disinfectant on-site areas.
- Spray booths or disinfectant walk-through booths are also used at the entrance to the site.
- Occupancy of rooms or common areas can be displayed and viewed.
- Covid19 mobile compliance app which includes chat-bots in multiple languages, are very helpful and should be introduced to employees.
- A control centre should be set up where you can use remote camera technology to track those who arrive to and leave the site.

13. Mental health
We need to be aware that Covid19 not only affects our physical health, but our mental health as well.
- We need to assist those who are suffering from anxiety or stress and support should be in place for those persons.
- This is also a time of uncertainty and many will need advice, support or just someone to talk to.

Additional important points
- Never mix any of the solutions or different types of disinfectants (e.g ammonia with bleach). Hazardous vapours will be released and can be very toxic.
- As hand sanitizers result in dehydration, we need to moisturise hands regularly.
- If any of the staff members develop skin rash or irritation after using disinfectants or the hand sanitizers, they are to inform occupational health practitioner/specialist immediately. They can then establish what the cause is and recommend another brand or type of sanitizer or disinfectant to be used.
.
Sources
Osha
Oshwiki
CIDB
Hseni
Lexology
Ehs Today Construction
Ehs Today Webinar
Hsa
CDC
Ontario
SA Builder
KPMG
PBC Today
To view more Articles, please visit our Leads 2 Business Blog.
If you are interested in becoming one of our subscribers, please visit Leads 2 Business.
To view notes with screenshots on how to use our website, please visit Leads 2 Business Wiki.
About Michelle Crosby
I started my journey at Leads 2 Business in the Directory Department in 2012. I was then promoted to the Private Projects Department in 2014 and was recently promoted to Projects HOD this year.
- Web |
- More Posts(30)