Christine and I arrived at Lanseria with a mix of excitement and nerves, unsure of what to expect from our meeting with Mr. Rampa Rammopo. His reputation preceded him, sharp, strategic, perhaps even formidable. Had we bitten off more than we could chew?
But the warm welcome at reception quickly put us at ease. And as we sat in ear shot of the boardroom, the sound of laughter from within – Mr. Rammopo mid-meeting confirmed what we hoped: this was going to be a conversation worth having.
What followed was more than an interview, it was a deep dive into a vision reborn.
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
A Dream on the Rise
Before the world was brought to a halt by an unforeseen pandemic, Lanseria International Airport stood on the brink of a bold transformation. There was an energy in the air, the kind that accompanies dreams backed by meticulous planning, solid capital projects, and an unrelenting belief in growth. LIA had cast its vision far and wide, anchored in a master plan designed to not only meet future demand, but to shape the airport into a regional powerhouse.
One of the key milestones in this ambitious blueprint was the expansion of the airport’s terminal building. This was no minor upgrade. With the expansion of the Pier, Lanseria increased its passenger handling capacity from 3 million to 4.5 million per annum. Simultaneously, the Multistorey Parkade (MSP) project had been completed and operational, the perfect complement to the expected passenger surge. Plans were also underway for a dedicated hotel, an upgraded fuel
farm. It was all happening…until it wasn’t!
Just as concrete was being poured and steel girders hoisted, the COVID-19 pandemic struck, grinding the global aviation industry to a near-total standstill. Dreams were paused, boardrooms fell silent and development projects hit a brick wall. But not all of them.
Some, like the expansion of the Pier, were already too far along to be abandoned. They had to continue, however cautiously. And with that, the tone shifted.Lanseria’s master plan didn’t dissolve. Instead, it evolved…
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Rising from Ruin – A New Blueprint for Resilience
Where many saw devastation, Lanseria International Airport saw recalibration. It wasn’t just about survival anymore. It became about adaptation, engineering a version of the airport that could thrive not just in normal times, but in uncertain ones too. This shift led to a full-scale strategic review of operations, with a central goal: “How can we re-purpose the airport to weather future storms?”
The answer lay in diversification.
One of the clearest opportunities identified was cargo, a market LIA had not tapped into before COVID. Traditionally, cargo operations at Lanseria were limited to the belly space of commercial airliners. But the explosion of e-commerce and the increasing demand for air freight made a
compelling case for a deeper play.Thus, the Lanseria Cargo Precinct is born.
Lanseria International Airport occupying a 90-hectare parcel of currently vacant land – with an additional acquisition of adjacent parcels under consideration, the precinct will be designed as a fully-fledged cargo ecosystem. This project alone is forecasted to claim between 20 to 30 hectares, targeting 5 -10% of Gauteng’s booming 400 000 ton per annum air cargo market. With preliminary designs complete and most regulatory approvals secured, Lanseria is gearing to break ground by Q4 2025. The project, estimated around R2 – R3 billion, is set to be a five – year phased development and a cornerstone of LIA’s post-pandemic legacy.
But the Cargo Precinct is just the beginning.
Tied to the cargo development is another strategic initiative: Maintenance, Repair, and Overhaul (MRO) facilities. With SAA Technical’s diminished presence at OR Tambo, a critical gap has emerged in regional maintenance services. Lanseria intends to fill it. Designs are done, funding is partially secured, and tender processes for construction are on the near horizon. This segment will not only serve operational needs but also open up new business avenues for the airport.
Another future-proofing initiative is the new Fuel Farm, which will boost LIA’s fuel storage capacity from 1 million to 4.5 million litres. Final designs have been submitted, and approvals from the City of Johannesburg; delayed but not derailed, are anticipated soon. This project plays a pivotalrole in supporting the increased aircraft activity expected in the years ahead, especially as morecarriers consider Lanseria as a viable base.
Next in line is the FBO (Fixed Base Operator) facility, currently in conceptual design stages. It’s a natural progression for Lanseria, which has long attracted business and private aviation. With market studies underway, the FBO project could soon become another defining pillar in Lanseria’s transformation, catering to elite travellers and specialized aviation services.
Add to this the Taxiway Alpha Upgrades, an estimated R200 million infrastructure investment aimed at enhancing the operational robustness of the airport’s air-side environment. With feasibility studies complete and consultants being appointed soon, construction is expected to be rolled out over 18 months to minimize disruption, ensuring the runway ecosystem matches thescale of LIA’s broader aspirations.
What unites these five capital projects: The Cargo Precinct, MRO, Fuel Farm, FBO facilities, and Taxiway upgrades, is not just ambition, but a sense of readiness. Readiness for growth. Readiness for disruption. Readiness for the future.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________
A Legacy in the Making
Together, these developments don’t just mark a recovery from the COVID-19 shock, they represent a powerful leap into a new era. For CEO Rampa Rammopo, these are not mere infrastructure upgrades; they are Legacy Projects: A visionary master-stroke shaped under pressure, re-imagined
during crisis, and executed with precision.
Over the next five years, Lanseria International Airport will transform into an active construction site, one parcel at a time, laying the foundation for the airport of tomorrow. An airport that’s resilient, diversified, and future-ready.
So whether you’re boarding FlySafair “For the Love of Flying,” or flying with any future operators who will inevitably be drawn to this revitalized hub – rest assured, Lanseria International Airport will be ready.
From the ashes of a global crisis, a bold new skyline is rising – and it’s taking off from Lanseria.
___________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Leads 2 Business | Written by Minnie Zondi
I am an insanely optimistic ambivert that does everything from the heart instead of the mind. Deeply interested in people and matters that pertain to mankind.






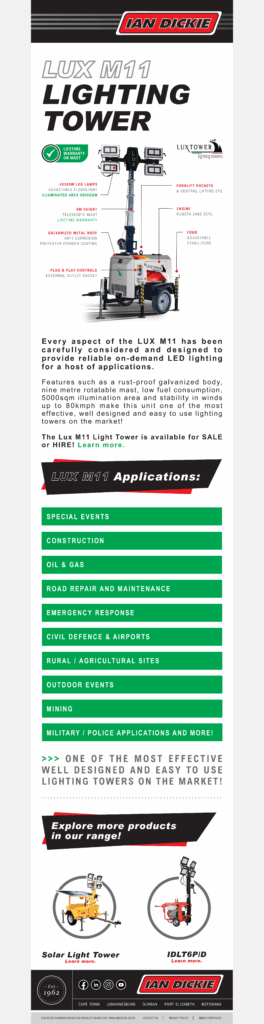
 Every aspect of the LUX M11 has been carefully considered and designed to provide reliable on-demand LED lighting for a host of applications.
Every aspect of the LUX M11 has been carefully considered and designed to provide reliable on-demand LED lighting for a host of applications.