
According to statistics recorded from August 2008 to July 2009, South Africa has 852 wastewater management plants. The question is though how many of those plants are still fully functional and how many work efficiently and fulfill their vital process? Below I will describe what the wastewater management process is as well as discuss some of the challenges faced.
What is waste water management?
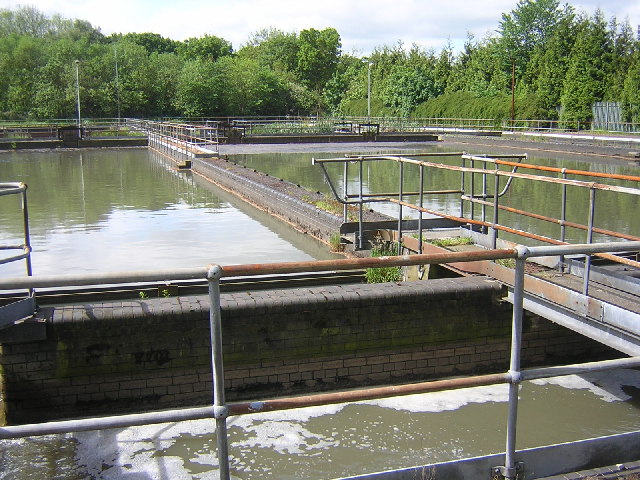
Wastewater management is an extremely important process that removes all the harmful components that may cause diseases from ‘sewage’ (as most South Africans would call it) water, in order to reproduce usable water again
- Alarming fact: Around 289,000 children under the age of five die every year from diarrhoeal diseases caused by poor water and sanitation. That’s almost 800 children per day, or one child every two minutes.
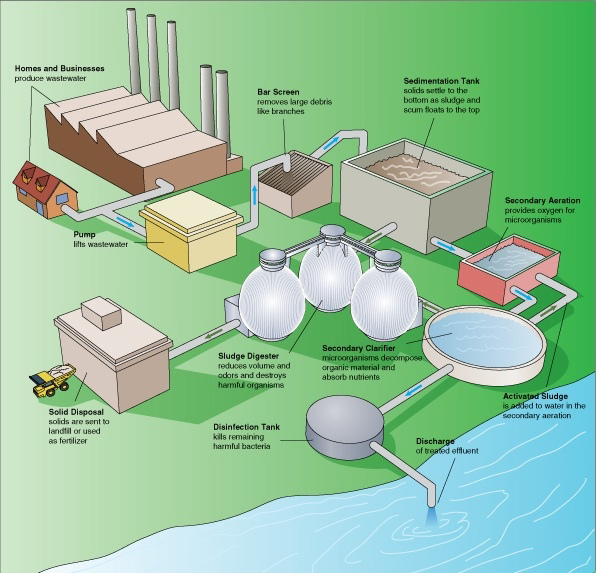
Steps to Wastewater Treatment:
1. Collection
- This is the first step whereby the municipality collects water through the collection system in place so that it all comes to and from a central point. (Drainage systems) Thereafter the wastewater is directed to the treatment plant.
2. Odor Control
- This is an extremely important step due to wastewater having many substances in that cause a stench over time and if not controlled it can affect the surrounding areas. Chemicals are used to reduce the smell.
3. Screening
- This is where all large objects are removed, such as nappies, sanitary towels, face wipes or earbuds as this may damage the equipment. This waste is transported to landfills once removed.
4. Primary Treatment
- This is where the macrobiotic (larger particles to be broken down) solid matter is removed. Wastewater is then transferred into tanks where the ‘sludge’ then settles on the surface in order to be removed by scrappers, moved to the centre and then extracted for further treatment
5. Secondary Treatment
- In this process, air is added to activated sludge (sewage containing micro-organisms) in order to further break down the particles. Air is pumped into tanks and mixed with the sludge. The oxygen consumes the remaining particles which cause the large particles to settle at the bottom of the tank. Wastewater passes through for a period of 3-6 hours
6. Bio-Solids Handling
- The solid matter gets directed to digesters which are heated to room temperature and treated for a month. Methane gases are produced which form nutrient rich bio-solids, this methane can be recycled and be used as a source of energy.
7. Tertiary treatment
- This stage has the ability to remove 99% of the impurities and is able to produce water at the standard of drinking but is extremely expensive and requires high skill and equipment as well as steady electrical supply, which we know is not readily available at this point.
8. Disinfection
- The water needs to be treated for at least 20-25 minutes in chlorine and sodium hypo chloride to remove the last bit of disease causing organisms. This is an integral part, hereafter the water is released for use.
Now that we have that long process out of the way, phew! We look at the fact that our water is not up to standard.
In a report, the DWS stated that there are extremely high levels of sewer pollution in our water due to the fact that we have dysfunctional treatment plants. How does this happen? I mean, I feel exhausted just reading that process, but it is pointed out how important each step is! Well… the following factors come into consideration: Plants are being poorly maintained, communities are growing at a rapid rate and infrastructure falling behind so these plants are operating above their capacity causing them to be overloaded.
Carte Blanche also recently did a program on the state of the treatment plants where they were following up on previous discussions they had had and most of these plants had failed because either nothing was done, or a facade was put up for a few months and then the plant returned back to normal or even worse than before.
Now my question is, how does this get resolved? Number one priority, in my opinion, is for these plants to firstly have some major upgrades done on them but obviously, that’s easy to say if you take the financial aspect out of it. Where should this money come from…
There are definitively some organisations trying to make a positive change and implement strategies and projects in order to succumb these challenges so feel free to check out the links for a positive change.
Sources:
The Process:
http://www.infrastructurene.ws/2013/05/24/wastewater-treatment-plants-in-south-africa/
http://www.conserve-energy-future.com/process-of-wastewater-treatment.php
The sad Truth:
http://www.infrastructurene.ws/2016/05/10/sas-waste-water-treatment-works-in-bad-shape/
http://www.infrastructurene.ws/2016/02/22/municipalities-rated-on-wastewater-management/
https://mg.co.za/article/2010-04-29-report-reveals-rotten-state-of-sas-sewage-plants
http://www.wateraid.org/what-we-do/the-crisis/statistics
Let’s bring back Positive change!










Leave a Reply